 |
| Fig. 1 Typical TOFD arrangement. |
Diffractions are separated in space so their reception by the receiving transducer is split by time. So, the difference in time can be used to locate and size cracks. A typical pattern of an ultrasonic signal which indicates the discontinuity shown in the upper image can be represented as:
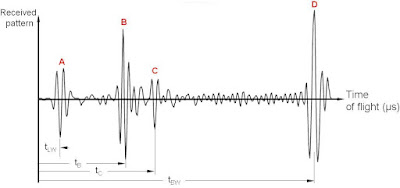 |
| Fig. 2. Pattern of pulses from a discontinuity with the TOFD method. |
Where:
- (A) represents the lateral ultrasonic wave travelling along the test object surface.
- (B) is a small pulse which represents the diffracted energy from the upper crack tip.
- (C) is the pulse received from the lower crack tips, and finally
- (D) is a large echo which corresponds to the reflection on the test backwall.
The TOFD technique has many other advantages over a pulse echo technique, such as, objectivity, repeatability and its speed. Moreover the method is insensitivity to weld surface conditions and discontinuity orientation. TOFD techniques are suitable for sizing; they accurately determine the length and depth of surface breaking and submerged cracks. The technique has also been used on nonplanar discontinuities. However the applicability of this technique may be limited because the lower crack tip may not always diffract enough energy to be detected.
No comments:
Post a Comment